Describe What Happens at a Dna Replication Fork During Replication
The DNA replication fork is where the replication origin forms the Y shape. As unwinding of the helix occurs during DNA replication tension is created ahead of the replication fork.

Solved 2 Describe What Happens During Dna Replication In Chegg Com
DNA polymerase performs DNA synthesis on the leading strand and RNA polymerase performs synthesis on the lagging strand.
. The replication fork textbf the replication fork the replication fork. Asked Sep 8 2016 in Biology Microbiology by lil_angel. Mutations can have serious effects on the function of a gene and an organism.
By breaking hydrogen bonds. The RF unwinds the unreplicated DNA ahead of it through a helicase enzyme complex Gambus et al. DNA helicases catalyze the break up of the hydrogen bonds between strands.
To achieve this each st View the full answer. Lesson Summary The replication fork is a very active area where DNA replication takes place. 11 During which phase of the cell cycle does DNA replication occur quizlet.
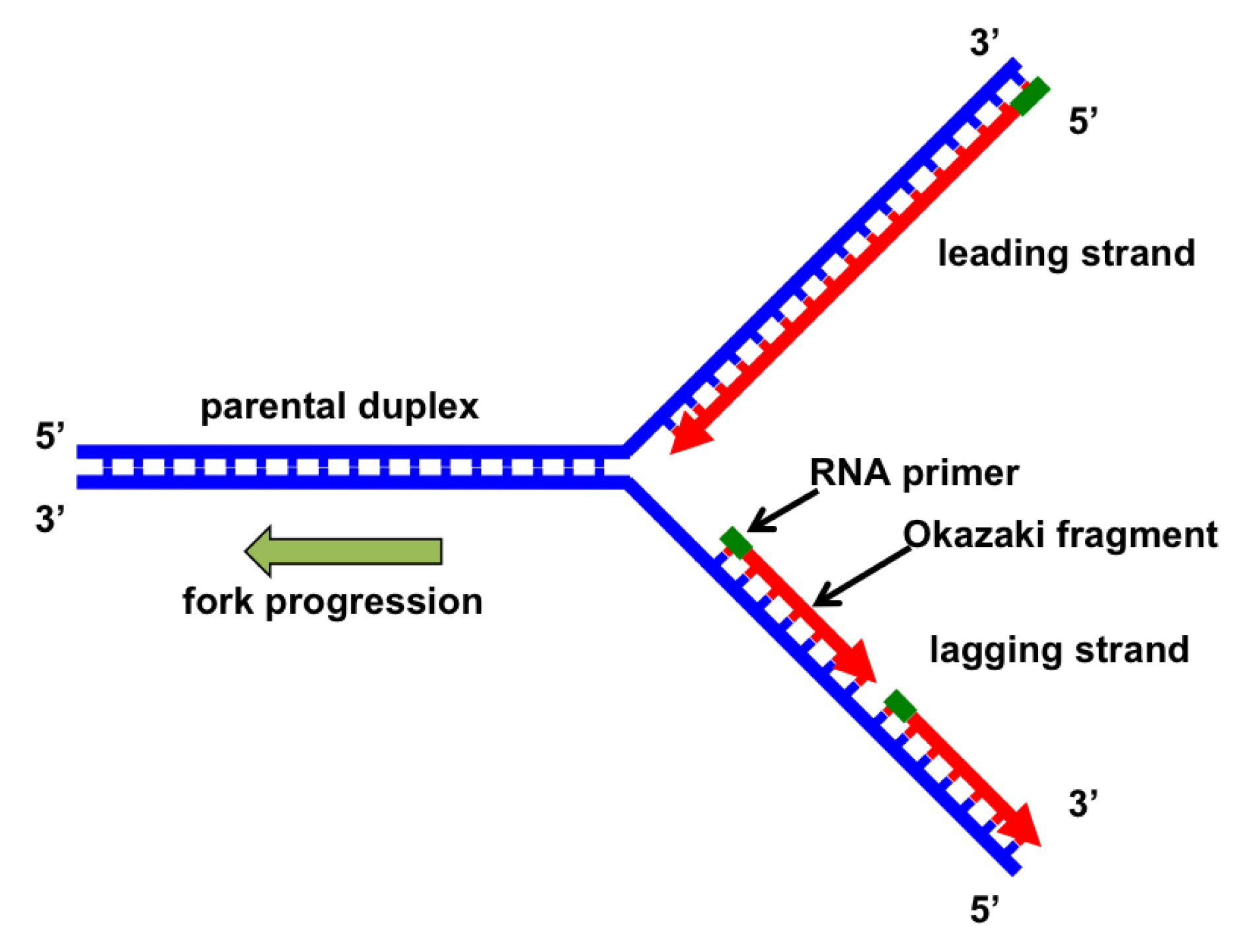
The Y-shaped region is called. The replication fork is a region where a cells DNA double helix has been unwound and separated to create an area where DNA polymerases and the other enzymes involved can use each strand as a template to synthesize a new double helix. An active zone of DNA replication moves progressively along a replicating DNA molecule creating a Y-shaped DNA structure known as a replication fork.
Two main activities happen at the fork. Complete and accurate replication once and only once per cell division cycle is essential to maintain genome integrity and prevent disease. The process of semiconservative replication suggested a geometry for the site of DNA replication a fork-like DNA structure where the DNA helix is open or unwound exposing unpaired DNA nucleotides for recognition and base pairing for the incorporation of free nucleotides into double-stranded DNA Figure 1.
RNA primase lays down an RNA primer to start DNA replication. 1 DNA replication It is the cycle by which a twofold abandoned DNA atom is duplicated to create two indistinguishable DNA particles. 14 At what stage.
13 What event occurs first during meiosis. DNA replication occurs in a series of five steps. The replication fork will continue to move down the DNA behind DNA helicase until the entire DNA is copied.
DNA synthesis by the replication fork is achieved with the enzyme DNA polymerase. Its synthesis slightly precedes the synthesis of the daughter strand that is synthesized discontinuously known as. This is a major problem not only for circular bacterial chromosomes but also for linear eukaryotic chromosomes which in principle could rotate to relieve the stress caused by the increased supercoiling.
The replication fork moves down the DNA strand to the strands. Describe the nature of this tension and state the manner in which it is resolved. When DNA polymerase reaches a primer from prior DNA synthesis the primer is removed and replaced with DNA.
2 DNA polymerase adds complementary nucleotides to the separated strand of DNA. It is also necessary for evolution and immune system response. DNA unwinding and DNA synthesis.
12 Which event first takes place during DNA replication. Its created when the strands are separated. Initiation at the origin of replication unwinding to expose the strands synthesis on both strands with many enzymes adding nucleotides 3 to 5.
The two arms of each Y Initially the simplest mechanism of DNA replication seemed to be the continuous growth of both new strands nucleotide by nucleotide at the replication fork as it moves from one end of a DNA. The DNA ahead of the replication fork has to rotate or it will get twisted on itself and halt replication. Impediments to replication fork progression including difficult to replicate DNA sequences conflicts with transcription and DNA damage.
1 An enzyme called helicase separates the DNA strands the space where they separate is called the replication fork. DNA primase - a type of RNA polymerase that generates RNA primers. Billions of base pairs of DNA must be replicated trillions of times in a human lifetime.
Describe what happens at a DNA replication fork during replication. Describe the nature of this tension and state the manner in which this tension is resolved. Primers are short RNA molecules that act as templates for the starting point of DNA replication.
It forms the replication fork by breaking hydrogen bonds between nucleotide pairs in DNA. DNA replication is an essential part of cell division as it ensures that each new cell has the same genetic information. This occurs in front of the replication fork and creates single-stranded DNA.
DNA replication is one of the most fundamental cycles that happens inside a cell. Firstly helicase enzymes separate DNA strands textbf helicase enzymes separate DNA strands helicase enzymes separate DNA strands. 10 Which process occurs during DNA replication.
DNA helicase - unwinds and separates double stranded DNA as it moves along the DNA. The DNA daughter strand that is synthesized continuously is known as the leading strand. Each of the two DNA polymerases adds nucleotides to a new DNA strand during replication at a single replication fork why are DNA repair enzymes important to an organisms survival an unrepaired error in DNA may result in a mutation.
DNA polymerase links DNA bases in the correct sequence according to complementary base pairing theory. A replication fork therefore has an asymmetric structure Figure 5-8. As unwinding of the helix occurs during DNA replication tension is created ahead of the replication fork.
The major functions of the replication fork are DNA unwinding and DNA synthesis.

When Dna Helicase Is Active The Result Is Study Com

Genes Free Full Text The Replication Fork Understanding The Eukaryotic Replication Machinery And The Challenges To Genome Duplication Html

No comments for "Describe What Happens at a Dna Replication Fork During Replication"
Post a Comment